
研究使用平台:NMT植物营养创新科研平台
期刊:Environmental Pollution
主题:NMT验证石墨烯基材料的植物毒性与其抑制**盐吸收相关
标题:Graphene oxide exposure suppresses nitrate uptake by roots of wheat seedlings
影响因子:5.714
检测指标:NO3-流速
检测样品:小麦
NO3-流实验处理方法:
培养3天的小麦苗在0/400mgL-1氧化石墨烯处理3天
NO3-流实验测试液成份:
6mM KNO3、2mM CaNO3、0.1μM MgSO4、0.1 mM NH4H2PO4
作者:浙江工商大学都韶婷、翁轶能
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
尽管有大量研究报告了石墨烯基材料的植物毒性,但这些材料对植物养分吸收的影响仍不清楚。
本研究表明,以200-800 mg L-1的氧化石墨烯(GO)处理的小麦植株的根部**盐浓度显着降低。无创微电极测量结果表明,GO可以显着抑制小麦根分生,伸长和成熟区的净NO3-流入。
进一步的分析表明GO可能被困在根的液泡中,并且最大根长度和侧根数量明显减少。另外,观察到根尖变白,起皱,氧化应激和呼吸减弱。这些观察结果表明GO非常不利于旺盛的根部生长,并且抑制了根部吸收面积的增加。
在分子水平上,GO暴露导致DNA损伤并抑制小麦根中大多数**盐转运蛋白(NRT)的表达,其中最显着下调的基因是NRT1.3,NRT1.5,NRT2.1,NRT2.3和NRT2 .4。
我们得出的结论是,GO暴露会降低根系吸收面积和根系活性,并降低NRT的表达,这可能因此抑制了NO3-吸收率,导致逆境植物中**盐的不利积累。
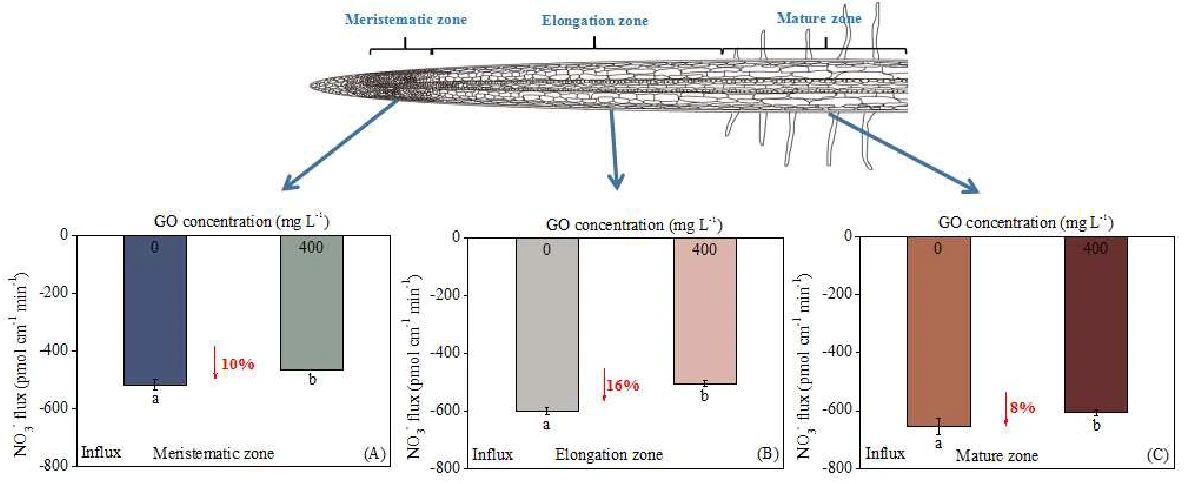
Effect of GO on the net NO3- flux in wheat roots. GO-precultured seedlings were transferred to the microelectrode system for net NO3- flow rate measurement. (A) meristematic; (B) elongation; and (C) maturation zones. Negative flux values indicate a net influx (One-way ANOVA, n = 3).
英文摘要
Despite the large number of studies reporting the phytotoxicity of graphene-based materials, the effects of these materials on nutrient uptake in plants remain unclear.
The present study showed that nitrate concentrations were significantly decreased in the roots of wheat plants treated with graphene oxide (GO) at 200-800 mg L-1. Non-invasive microelectrode measurement demonstrated that GO could significantly inhibit the net NO3- influx in the meristematic, elongation, and mature zones of wheat roots.
Further analysis indicated that GO could be trapped in the root vacuoles, and that the maximal root length and the number of lateral roots were significantly reduced. Additionally, root tip whitening, creases, oxidative stress, and weakened respiration were observed. These observations indicate that GO is highly unfavorable for vigorous root growth and inhibits increase in root uptake area.
At the molecular level, GO exposure caused DNA damage and inhibited the expression of most nitrate transporters (NRTs) in wheat roots, with the most significantly downregulated genes being NRT1.3, NRT1.5, NRT2.1, NRT2.3, and NRT2.4.
We concluded that GO exposure decreased the root uptake area and root activity, and decreased the expression of NRTs, which may have consequently suppressed the NO3-uptake rate, leading to adverse nitrate accumulation in stressed plants.
关键词:非损伤微测技术,NO3-流速,小麦
